Hairpins: Double Pipe and Multitube Heat Exchangers
Metalforms Heat Transfer hairpin heat exchangers are the industry standard for efficient performance and proven reliability. Backed by decades of combined engineering and manufacturing experience—and available in both double pipe and multitube configurations—our innovative designs and unique closures are a key element of more economical designs that offer ongoing operational savings. Learn more about putting the industry-leading expertise of Metalforms Heat Transfer and the performance advantages of our hairpins to work for you.
CONTACT US
Call us today to speak with one of our heat transfer specialists: (+1) 713.466.3535 or click to contact us below:
After-Hours Parts Support
inquiry@metalformsht.com

Benefits
Cost Effective
In many applications, performance can be achieved by a single hairpin as opposed to multiple Shell & Tube exchangers, resulting in lower capital costs, as well as future maintenance.
Cyclic or Shock Service
Large-radius U-bends and all terminal connections located at the same end allows for more extreme thermal expansion without the need for an expansion joint.
Durable Baffle Cage
Baffles are welded to tie rods without “sleeves” or internal nuts.
Extreme Terminal Temperature Differential
Independent-tube sheets and closure components eliminate differential thermal expansion across a single-tube sheet design, as is typically encountered with conventional Shell & Tube.
High Pressure
Our unique closure technology allows for pressures exceeding 10,000 psi.
Large-Radius U-Bends
Easy to clean, and eliminates the need for expansion joints or packed joints.
Moveable Support Brackets
Allow shell expansion and contraction; eliminate sliding plates; slotted on all four sides for flexible installation and future additions.
Separate Tube Sheets
Handles high temperature differences and cycling more effectively.
Small Footprint
Due to the geometry of hairpins, the equipment takes up less space relative to the Shell & Tube alternative.
Temperature Cross
Ideal when a temperature cross exists, or a close temperature approach is desired due to its single-pass configuration that allows for true countercurrent flow.
Common Applications
- Fuel gas heaters
- Lean - rich glycol exchangers
- Lean - rich amine exchangers
- Lean - rich CO2
- Gas coolers
- Well stream heaters
- Intercoolers
- Aftercoolers
- Heat Affluent Exchangers
Features
Enhancement Devices
The use of Metalforms Heat Transfer enhancement devices, such as inserts, baffles, and TWISTED TUBE® Bundle technology can increase the effectiveness of engineered equipment.
External Bolting
The external bolting allows for tightening of bolts while in operation without having to remove any covers or the tube bundle.
Internal Terminal Closure
The independent closures on both shell side and tube side result in smaller flange designs. Our unique closures allow for more economical and efficient designs. Contact us or request a quote to Find out more how KHT Hairpins can help you.
Robust Aftermartket Support
Metalforms Heat Transfer maintains a dedicated aftermarket support staff that is available for your repair, replacement, and spare part needs.
Single-Pass Design
The single-pass design allows for even distribution of expansion forces across the tube sheet.
Wide Range of Sizes
Hairpins are a versatile product with compact designs that are typically more effective than large Shell & Tube designs. Sizes range from 2” O.D. to 40” O.D. shell legs.
Closures
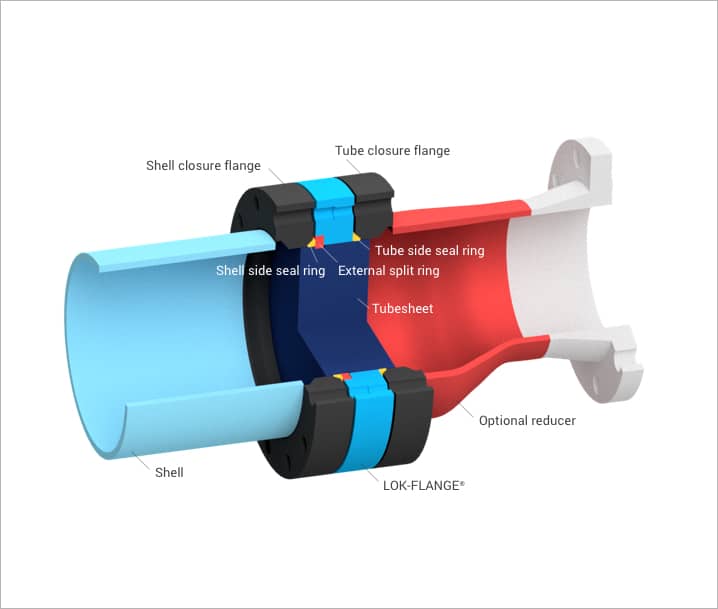
LOK-FLANGE® Closure
The LOK-FLANGE® closure uses common through-bolting with independent gaskets and is typically used for design pressures below 1,000 psi. The center flange of this closure is threaded, which allows removal of the tube-end flange for inspection and cleaning of the tubes while maintaining pressure on the shell side. This closure allows the maximum number of tubes in a given shell diameter.
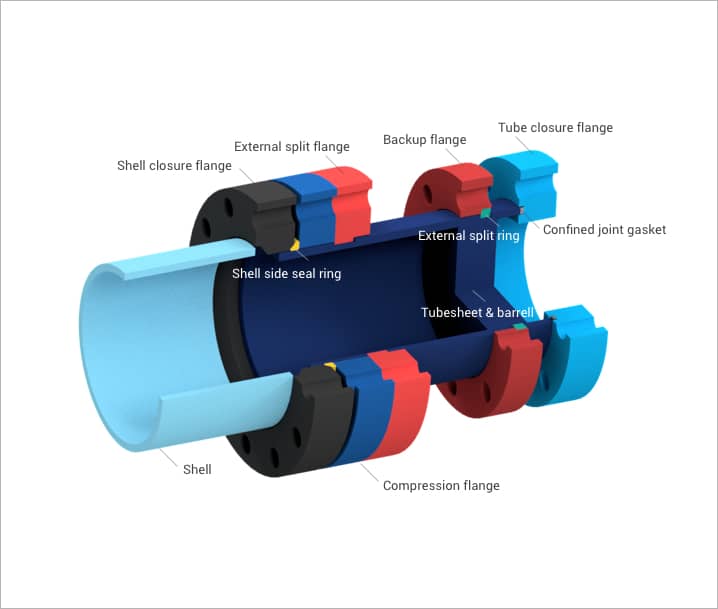
Separated head Closure
The separated head closure uses independent shell-side and tube-side closures. This is ideal in cyclic and shock service, high temperature, and mid-pressure applications.
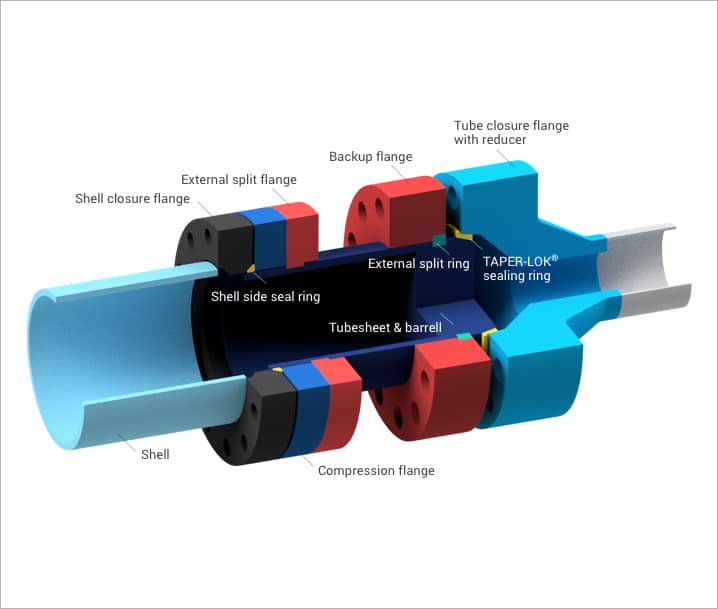
Taper-Lok® Closure
Our TAPER-LOK® closure is typically used for high-pressure applications exceeding 10,000 psi (1055 kg/cm2). Like our separated-head, the TAPER-LOK® closure uses separate tube-side and shell-side flanges, bolting, and gasketing. The unique feature this closure offers is a reusable TAPER-LOK® ring, which acts as a self-energizing seal.
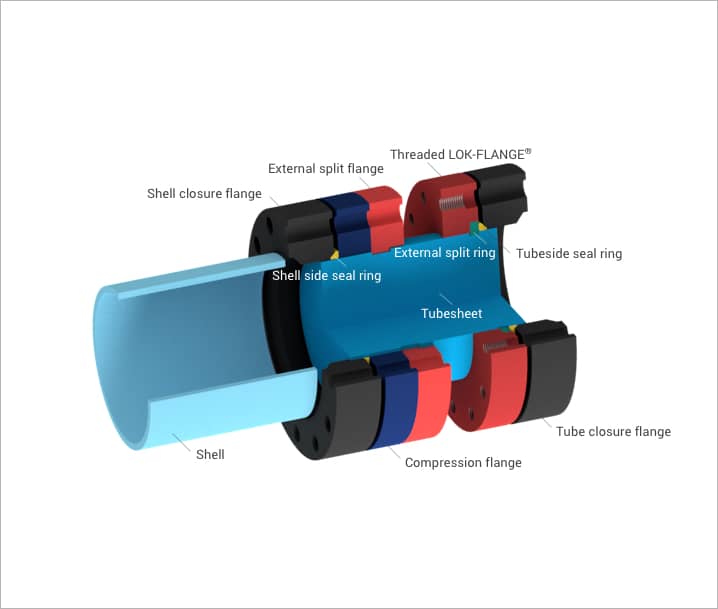
ZR™ Closure
The ZR™ Closure bridges the gap between the separated-head and the LOK-FLANGE® closure by providing separate tube-side and shell-side flanging and bolting, while retaining the maximum number of tubes in a given shell diameter.




